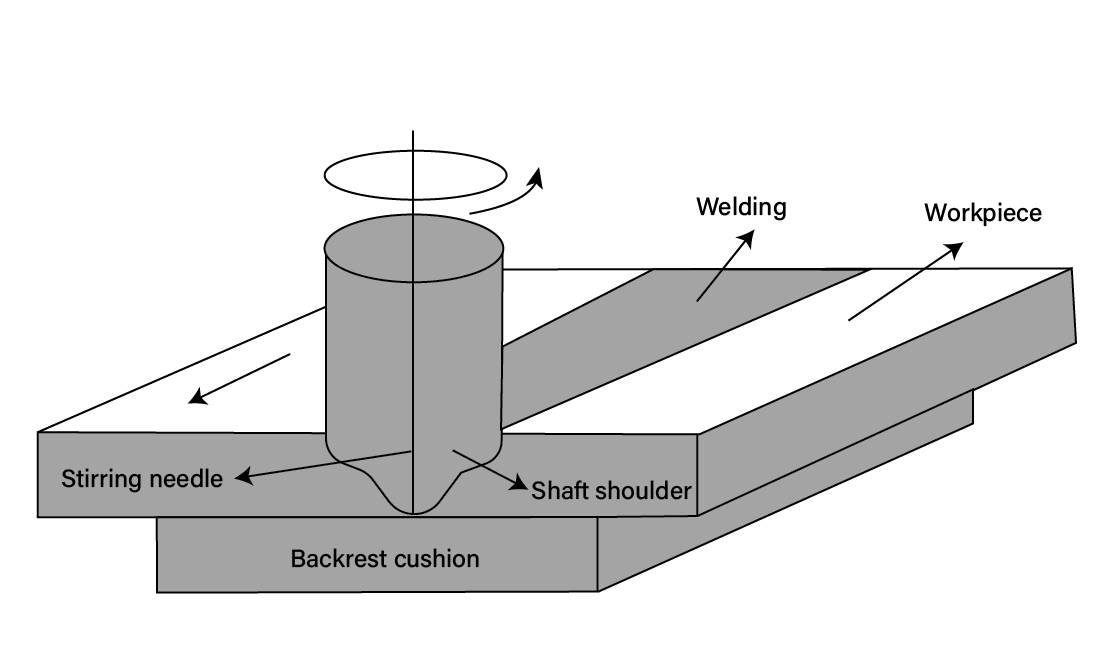
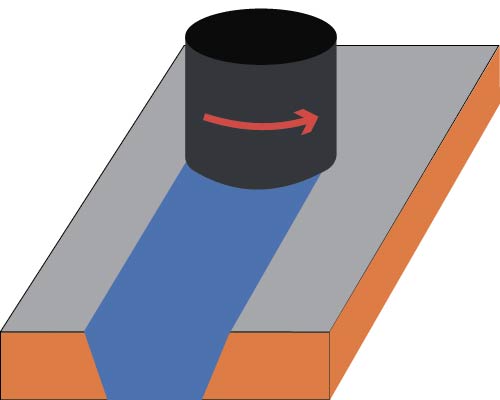
Friction Stir Welding Principle
The principle of friction stir welding is similar to conventional friction welding, as it also utilizes friction heat and plastic deformation heat as the heat source for welding. The difference lies in the fact that in the friction stir welding process, a cylindrical or other shaped (such as a threaded cylinder) welding pin is inserted into the seam of the workpiece. Through the high-speed rotation of the welding head, it is brought into frictional contact with the material of the workpiece, thereby raising the temperature and softening the material at the joint. At the same time, material is subjected to stirring friction to complete the welding.