What are the differences between liquid-cooled and air-cooled battery plates?
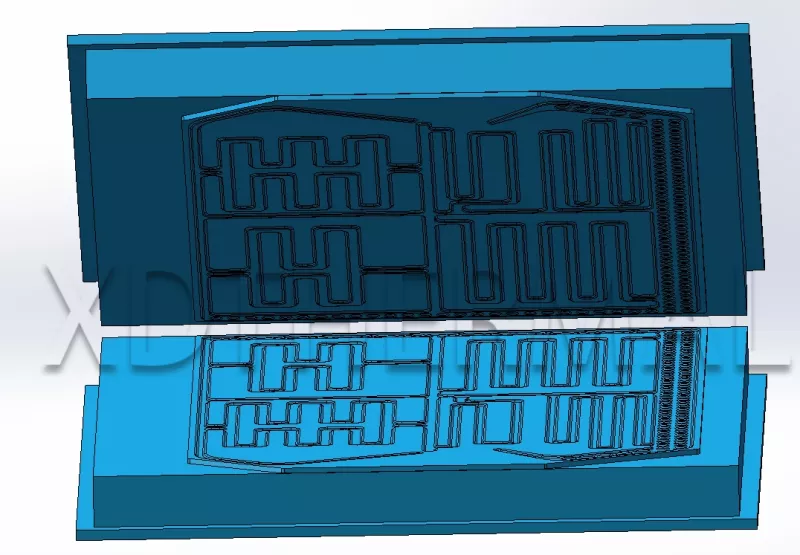
What are the differences between liquid-cooled and air-cooled battery plates? Choosing the right battery cooling system can be a daunting task. Misunderstanding the differences might lead to inefficient thermal management and reduced battery life. Let’s uncover the key distinctions to help you make an informed decision. Liquid-cooled battery plates offer superior heat dissipation using coolant circulation, ideal for high-performance needs like EVs. Air-cooled plates rely on airflow for cooling, making them cost-effective for moderate or lower thermal requirements. The choice depends on efficiency needs, cost considerations, and specific applications. Ready to delve deeper? Let’s explore these systems from an engineer’s perspective. Table of Contents Introduction to Battery Cooling Systems As batteries become more integral to modern technology—from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage—the need for effective thermal management has never been greater. Cooling systems are essential to maintain optimal battery performance and ensure safety. Battery cooling systems prevent overheating, which can degrade battery life, reduce efficiency, and pose safety risks. Two primary methods dominate the industry: liquid cooling and air cooling. Each has its unique mechanisms, advantages, and drawbacks. What is the difference between liquid-cooled and air-cooled? As an engineer, buyer, researcher or others, understanding the fundamental differences between liquid-cooled and air-cooled systems is crucial. Each system offers unique advantages depending on your application’s demands. Liquid cooling circulates coolant to absorb and dissipate heat efficiently, suitable for need efficient heat dissipation under heavy loads, high ambient temperatures, high-power devices,concentrated heat sources , or tight space constraints scenarios. Air cooling relies on airflow(either forced by fans or natural convection) over the battery surface, ideal for less intensive applications due to its simplicity and lower layout and maintenance costs. In liquid-cooled systems, a coolant flows through channels in the battery cooling plate, absorbing heat directly from the battery cells. This method ensures…